Why do people follow the dairy-free diet? When do you recommend dairy-free meal plans to clients? This article will explore everything about a dairy-free diet, including a food list, dairy substitutes, recipes, and meal planning.
What is the Dairy Free Diet?
A dairy-free diet is a way of eating that eliminates all sources of dairy products, including milk, cheese, yogurt, and other milk-derived products.
Why do people go on a dairy-free diet?
People may choose to adopt a dairy-free diet for various reasons. Some do it due to health issues such as lactose intolerance and milk allergy.
Additionally, some people choose to avoid dairy for ethical reasons, such as concerns about animal welfare in the dairy industry. Furthermore, there is a growing trend of people eliminating dairy from their diets due to perceived health benefits, although scientific evidence on this is mixed.
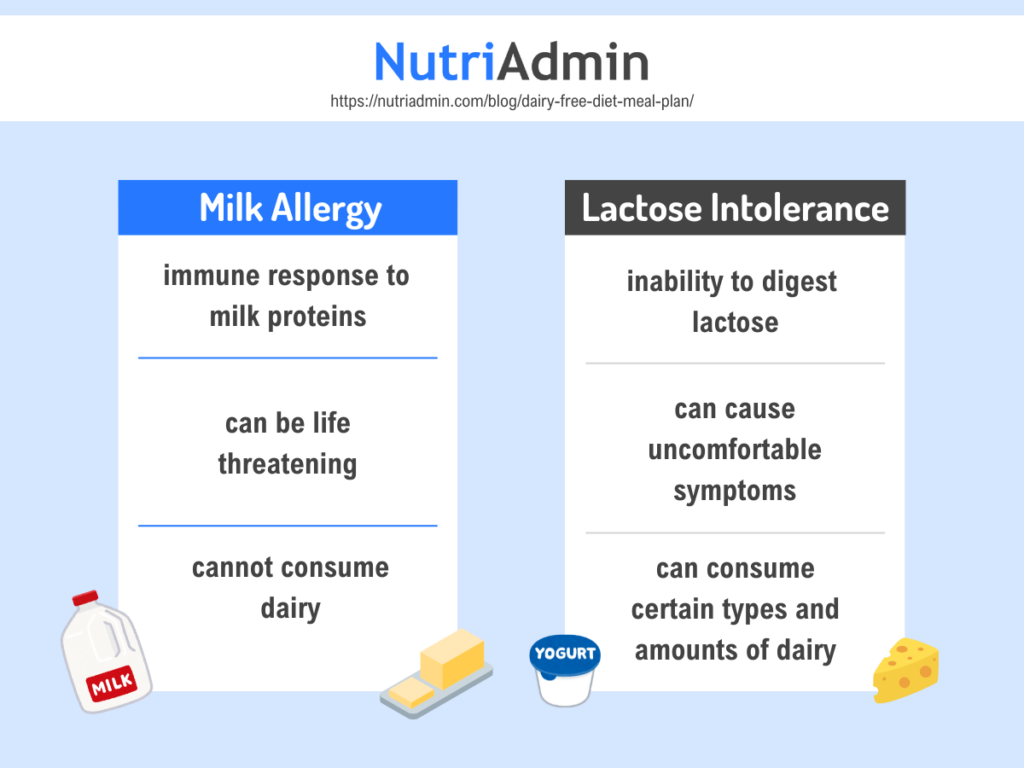
Milk Allergy
In developed countries, the prevalence of milk allergy in children younger than 3 years old is 2 to 3%. This is common in babies and young children. Although it is rare, some people do not outgrow their milk allergy, which persists into adulthood.
Dairy allergy is an adverse response to the proteins found in milk and dairy products. When someone is allergic to dairy, their immune system treats milk and other dairy products as harmful threats, triggering an allergic reaction.
Milk allergy symptoms can include:
- digestive issues
- vomiting
- skin rashes
- respiratory problems
- bloody stools
- anaphylactic shock
Milk Allergy Management
Individuals with a milk allergy should avoid consuming milk and dairy products. It’s important to carefully read labels to steer clear of inadvertently consuming foods containing hidden dairy.
If advised by their medical practitioner, people with milk allergies should carry an epinephrine auto-injector. If a child has a milk allergy, teachers and caregivers should be notified about their condition. It’s important to educate the individual and their caregivers on how to use the auto-injector in case of emergencies.
Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance affects approximately 65% of the world’s population, making it one of the most common food intolerances.
It is a condition in which the body is unable to fully digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. Lactose intolerance occurs when the small intestine doesn’t produce enough lactase, a digestive enzyme that breaks down lactose in food so that the body can absorb it.
Consuming lactose-containing foods can lead to symptoms such as:
- bloating
- diarrhea
- stomach cramps
Lactose Intolerance Management
Unlike people with milk allergy, individuals with lactose intolerance don’t need to eliminate dairy from their diet. Instead, they can:
- Drink small amounts of milk gradually and make sure to have it with meals.
- Incorporate dairy into your diet gradually in small quantities, and observe how your body responds.
- Consider consuming yogurt and hard cheeses such as cheddar or Swiss, as they contain less lactose compared to other dairy products.
- Use lactase supplements to aid in the breakdown of lactose found in dairy products.
Some people mistakenly interchange milk allergy with lactose intolerance, but they differ completely.
Ethical and Environmental Reasons
Vegans avoid dairy for several reasons. One of the primary reasons is a concern for animal welfare, as many oppose the practices of industrialized dairy farming and the separation of calves from their mothers. Environmental impact is another factor, as the dairy industry has been associated with issues such as greenhouse gas emissions.
Health reasons also play a role, as some vegans avoid dairy due to concerns about lactose intolerance, saturated fats, and potential links to certain health conditions. Lastly, ethical considerations related to animal exploitation and the belief that animals should not be used for human consumption also contribute to this dietary choice.
Health Concerns
Some people avoid dairy products because they mostly contain saturated fat, which is known to raise LDL cholesterol levels.
Is it really necessary to avoid dairy? No, omitting milk and dairy items from your diet can potentially do more harm than good because they are important components of a nutritious and well-rounded diet.
It is recommended by the American Heart Association to strive for a dietary plan that results in 5% to 6% of calories coming from saturated fat. This means that you can still enjoy dairy products as part of your diet, but it’s important to consume them in moderate amounts.
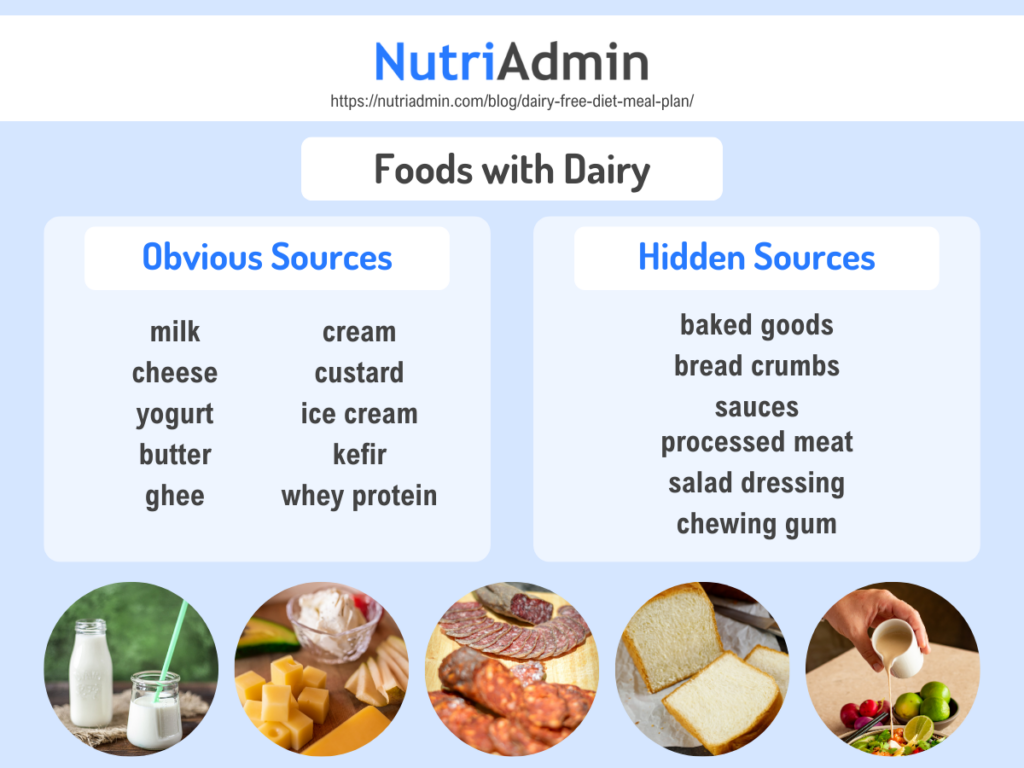
What foods contain dairy?
Milk and milk products such as cheese, yogurt, and cream are easily recognizable as dairy, but there are also less obvious food items that contain dairy. Baked goods, sauces, salad dressings, chewing gum, and processed foods may contain dairy. Always check the label to confirm if your food contains dairy.
Dairy-Free Food List
Whole foods are the most reliable choice for those with a dairy allergy or lactose intolerance, as they are free from dairy. In addition to whole foods, vegan options also offer a wide variety of dairy-free choices.
- vegetables
- fruits
- meat
- poultry
- eggs
- fish
- seafood
- beans and legumes
- nuts and seeds
- whole grains
- herbs and spices
- oils (olive oil, avocado oil)
- dark chocolate
Dairy-Free Diet Meal Plan
Creating meal plans for clients with milk allergies or lactose intolerance can be time-consuming for nutritionists, personal trainers, or coaches who are used to including dairy products like yogurt and cheeses. However, making substitutions for dairy is essential in such cases.
- Dairy Milk – soy milk, oat milk, almond milk, coconut milk, and other plant milk.
- Yogurt – almond yogurt, coconut yogurt, soy yogurt, cashew yogurt.
- Butter – coconut oil, olive oil, vegan butter, (for baking) apple sauce, avocado, mashed bananas, nut butter.
- Cream – coconut cream, silken tofu, cashew cream, and other non-dairy creams.
- Cheese – vegan cheese, nutritional yeast.
Dairy-Free Diet Planner
NutriAdmin is a nutrition software with a meal plan generator that also functions as a dairy-free diet planner. It has a diet filter that automatically removes dairy from meal plans, simplifying the creation of dairy-free meal plans for nutrition and fitness professionals in just 60 seconds.
You can use and download the dairy free meal plan below generated through NutriAdmin’s meal plan generator.
Dairy-Free Recipes
Aside from a diet planner, NutriAdmin also offers a nutritionist-vetted recipe database. Here, nutrition and fitness professionals can find dairy-free recipes that are both delicious and easy to make. Below are sample dairy free recipes from NutriAdmin:
Potential Risks of a Dairy-Free Diet
Dairy products provide essential nutrients for energy, growth, development, and bone health. If you want to eliminate them from your diet, make sure you get enough of these nutrients from other sources. Additionally, you should consult your healthcare provider if you need to take supplements.
The following are nutrients that can be found in dairy:
- Calcium
- Phosphorus
- Protein
- Vitamins A, D, and B12
- Riboflavin
- Potassium
- Zinc
- Choline
- Magnesium
- Selenium
To ensure you get enough of these nutrients when eliminating dairy from your diet, it’s important to consume a variety of foods and consider fortified non-dairy alternatives. Here are some examples of non-dairy alternatives for Calcium and Vitamin D that you can add to your diet if you don’t want or can’t consume dairy.
Non-Dairy Calcium Alternatives
- tinned fish with bones
- non-dairy milk fortified with Calcium
- tofu made with calcium sulfate
- green leafy vegetables
- hummus
- eggs
- figs
- almonds
- sesame seeds
- tahini
Non-Dairy Vitamin D Alternatives
- Exposure to sunlight on your skin helps your body produce vitamin D.
- mushrooms
- Rainbow trout, freshwater
- salmon
- Vitamin D-fortified food and drinks
Summary
Dairy-free meal plans and recipes are for individuals who avoid dairy due to milk allergy, lactose intolerance, ethical beliefs, or health concerns. A dairy-free diet means not consuming milk, cheese, yogurt, and other foods made from dairy. To make balanced dairy-free meal plans, focus on natural foods like fruits, vegetables, lean meats, beans, and grains.
Use dairy alternatives like plant-based milk, non-dairy yogurts, and vegan cheeses. When making dairy-free recipes, use substitutes like coconut oil or plant-based butter for baking and nutritional yeast for a cheesy taste. There are many options for a dairy-free diet, such as fresh produce, plant-based proteins, and healthy fats. Be careful of hidden dairy in processed foods, and always check the labels.
When making dairy-free diet plans, make sure to get enough calcium and vitamin D from fortified alternatives or other foods. With careful planning and creative recipes, a dairy-free diet can be both nutritious and enjoyable.