Are you still using BMI to assess your clients’ current nutritional status? How confident are you that your existing assessment methods and questionnaires are sufficient to understand your clients’ current health status? Do you want to provide a more comprehensive and effective fitness or nutrition plan for your clients? In this detailed guide, we will cover various body composition analysis methods that you can use, such as skinfold tests, Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA or DXA), and bioelectrical impedance analysis scans like InBody, guiding you through the benefits, differences, and costs.
Understanding Body Composition
In fitness and health, the saying “you are what you eat” often translates to “you are what you measure”. With technological advancements, the term “body weight” can now expand to include an intricate web of metrics that provide a more detailed information known as body composition. This evaluation provides valuable insights to nutritionists, coaches, and personal trainers by revealing a comprehensive view of an individual’s health and fitness potential.
Body composition refers to the percentages of fat, bone, and muscle in the human body. It is important to have a healthy balance of these components for overall health and fitness.
BMI vs Body Composition
BMI, or body mass index, has been widely used as a measure of body composition. However, it only takes into account a person’s weight and height, and does not consider their body fat percentage, muscle, or bone mass.
This means that someone with a normal BMI may still have an unhealthy level of body fat. This is why it is important to also assess body fat percentage when evaluating an individual’s body composition.
A person can be considered skinny fat or have normal weight obesity with a normal BMI but high body fat percentage. Conversely, a higher BMI could indicate more muscle mass and lower body fat percentage. This is because muscle tissue is denser than fat tissue, making it necessary to assess body fat in order to accurately understand one’s body composition and make appropriate health recommendations.
Body Composition Scan
A body composition scan evaluates the relative amounts of different body tissues such as fat, muscle, and bone.
Unlike regular scales measuring only weight, body composition scans reveal tissue distribution for a more detailed analysis. This level of precision is especially significant for athletes, older adults, and those on a weight loss or bodybuilding journey.
The Science Behind the Scan
Body composition scans are grounded in various scientific methods, the most common being bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA or DEXA), and anthropometric measurements.
These techniques differ in the extent of detail and, consequently, in their accuracy and applications. Each method uses a distinct approach to measure body composition, whether it’s through passing electrical currents, X-ray imaging, or simple body dimension assessments. It’s important to understand that while all are valid, they serve different purposes and yield varying degrees of precision.
The Benefits of Body Composition Scans
Body composition scans are a valuable tool for understanding your body’s makeup and overall health. Here are some of the key benefits they offer:
- More reliable way of measuring body fat percentage, muscle mass, and bone density.
- Provides insight into your metabolic rate and overall metabolism.
- Allows for tracking progress towards fitness or weight loss goals which can result to increased motivation to lose weight or achieve goals.
- Can identify imbalances in muscle development or skeletal structure.
- Helps to determine risk factors for chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
- Offers personalized recommendations for nutrition and exercise based on individual results.
As a nutrition or fitness professional, this assessment can help you plan on how to make a meal plan that aligns based on your clients’ goals and body composition results. If your client is trying to lose weight, this can help you formulate an appropriate intervention plan whether in terms of workout routines or nutrition education, such as giving calorie deficit tips.
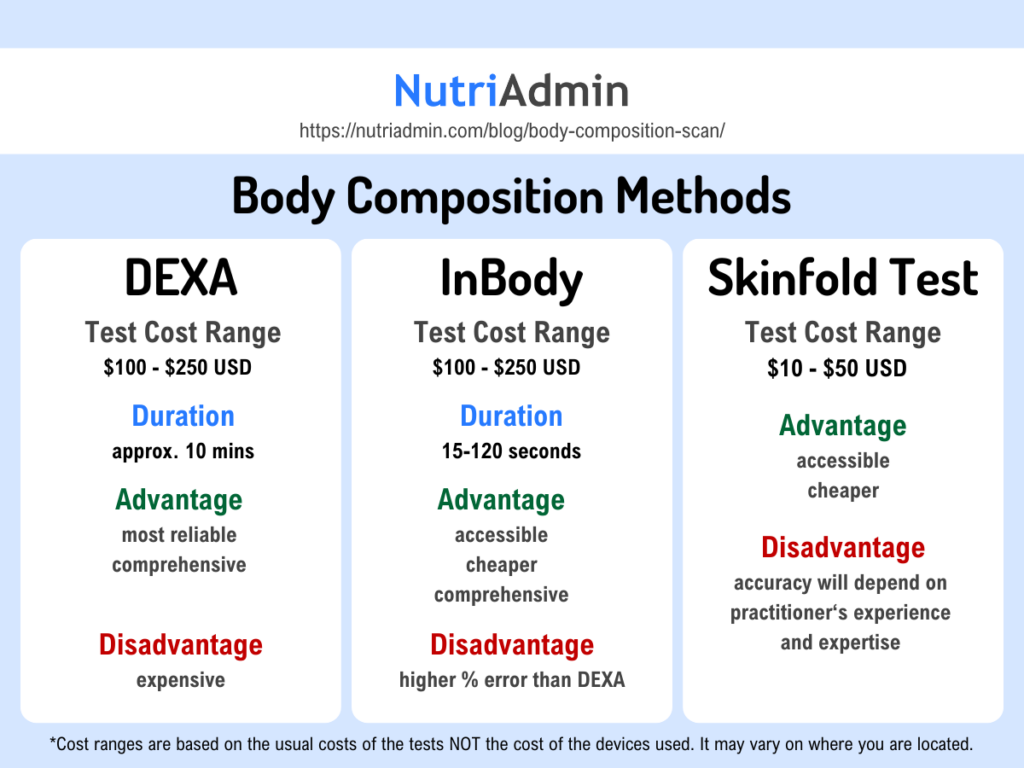
Skinfold Test
Skinfold test, also known as skinfold caliper measurement or pinch test, is a commonly used method for assessing body fat percentage. It involves taking measurements of skinfold thickness at specific sites on the body using a skinfold caliper.

Trained professionals like personal trainers, fitness instructors, and healthcare providers can perform this test. However, it is important to note that the accuracy of the results may vary depending on the skill and experience of the person performing the test.
To perform a skinfold test, a skinfold caliper is used to measure the thickness of folds of skin at various locations on the body. The most common sites measured are the triceps, biceps, subscapular (shoulder blade), and suprailiac (hip). An equation then uses these measurements to estimate body fat percentage.
There are different types of skinfold calipers available in the market, including Lange and Harpenden calipers. Some models have additional features such as automatic calculations or digital display for easier use.
One of the main benefits of using a skinfold test is its low cost compared to other methods such as DEXA scans or hydrostatic weighing. It is also non-invasive and does not require any special equipment or preparation.
However, there are some limitations and potential sources of error with this method. Factors such as improper technique or variations in measurement sites can affect the accuracy of results.
DEXA body composition scan
Dual X-ray Absorptiometry, commonly known as DXA or DEXA, is one of the gold standards in body composition analysis. It is highly regarded for its accuracy and comprehensive analysis. A DEXA or DXA body composition scan is a non-invasive procedure. It uses low-dose X-rays to accurately measure the amount of fat, muscle, and bone in your body. Trained healthcare professionals typically perform it at specialized facilities.
Another benefit of a DEXA body composition analysis is the ability to provide detailed information about different areas of the body. This can be useful for tracking changes in body composition over time and identifying potential health risks.
The DEXA scan procedure is quick and painless. It has the ability to differentiate between types of fat (such as visceral or subcutaneous) for a more comprehensive understanding of overall health.
However, there are also cons to consider. A DEXA scan can be costly and insurance may not cover it. Furthermore, while low-dose radiation is generally safe for most individuals, it might pose some risks.
BIA Composition Scans
Bioelectrical Impedance (BIA) is a way of measuring body composition by using electrical currents to distinguish between fat mass and fat-free mass.
This is based on the fact that each tissue type has different electrical properties due to varying water content. BIA uses this information, along with demographic data (such as height, weight, age, and sex), to estimate body composition.
However, it’s crucial to assess the reliability and accuracy of these tools before relying on them for decision-making on interventions.
BIA tends to underestimate body fat percentage and fat mass in lean individuals. It may overestimate those with higher levels of adiposity.
One major advantage of BIA scans is their affordability. Unlike methods like dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), this doesn’t need costly equipment or trained personnel.
BIA scans are easily accessible as they can be performed in most health clinics and fitness centers. They also provide results quickly, making them convenient for regular monitoring.
InBody Composition Scan
InBody is a known brand offering bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) devices. According to their website, an InBody test can quickly and accurately analyze your body composition, showing the amounts of muscle, fat, and water in your body. It provides easy-to-understand measurements on a Result Sheet within 15-120 seconds depending on the model.
A 2022 study states that InBody composition scans are good alternatives when DXA body composition analysis is not available, but they may have some small errors. Practitioners should be aware that there is a consistent difference in results for all comparisons and a difference related to body fat mass for women and muscle mass for men.
In another 2022 study on the reliability and validity of BIA devices like Inbody, researchers found that while these devices exhibited acceptable within-session reliability. However, you should exercise caution when using them to assess body fat percentage. This is because they demonstrated insufficient agreement when compared to DEXA scans.
How to Find a Body Composition Scan Near Me
Nutritionists and coaches would find it beneficial to be aware of the closest testing centers offering DEXA or Inbody scans. This knowledge allows you to recommend specific locations to your clients when requesting body composition scan results, offering them added convenience by eliminating the need for independent searches.
InBody offers a dedicated page that can help you locate the nearest testing center in your location.
For DEXA body composition scan, you can make a quick Google search using the following keywords:
- DEXA scan near me
- DEXA scan [insert your location]
Understanding the Costs
Cost can be a significant deterrent for many when considering body composition scans or other analysis methods. DEXA scan costs are typically higher than those of an InBody scan and skinfold tests, reflecting the former’s clinical-grade equipment and including the added value of bone density measurement.
Based on the top Google search results for US, DEXA can cost between $100 and $250 USD. In contrast, InBody tests can cost between $100 and $250 USD. The Skinfold Test is the cheapest option, costing $10 to $50 USD.
Conclusion
Body composition scans present transformative methods in understanding a person’s fitness and health status. In this article we’ve discussed three types namely skinfold tests, DEXA, and bioelectrical impedance analysis.
Skinfold tests are cost-effective and non-invasive, but their results depend on the skill level of the practitioner. On the other hand, DEXA scans offer precise and comprehensive results, yet they can be costly. Lastly, bioelectrical impedance analysis, including InBody, is affordable and easy to access, but could potentially provide less accurate results.
These advanced body composition analysis methods reveal more than just weight, offering insights to fat percentages, muscle mass, and bone density. This vital information enables nutritionists, personal trainers, and coaches to create more accurate, personalized fitness or nutrition plans targeting their clients’ unique needs and goals.
By adopting these tools, professionals in the field can deliver an enhanced level of care, offering comprehensive solutions to their clients. This, in turn, can lead to significant results aligned with their health or fitness goals.