The DASH Diet meal plan was first introduced in 1997. Since then, many studies have confirmed its effectiveness, and several organizations have ranked it as one of the best diets in the world.
But what makes this diet special?
Well, it is very effective against hypertension (high blood pressure), and many experts also recommend the diet as a healthy way of eating, even for those without hypertension. Hypertension is a serious illness that can lead to many other diseases in the brain, lungs, kidneys, and the heart.
In fact, over the last 5 decades, there has been a steady rise in diseases such as hypertension, obesity, diabetes, and coronary heart disease. World Health Organization reports that an estimated 1.28 billion adults all over the world have hypertension, and more than 4 in 10 of these people are unaware that they have hypertension.
Of course, it is unsurprising that only 42% of adults with hypertension are even diagnosed and treated. Of those treated, only 1 in 5 adults diagnosed with hypertension have it under control.
With these statistics, it is evident that hypertension is a menace all over the world. Little wonder it is a major cause of premature death all over the world.
What is Hypertension?
According to the American Heart Association, hypertension occurs when the force of blood that flows through the blood vessels becomes consistently elevated over time.
Hypertension is known as a silent killer because it does not present with clear or specific symptoms. Hence, many people carry on their normal activities without knowing their blood pressure is high until a major adverse event occurs.
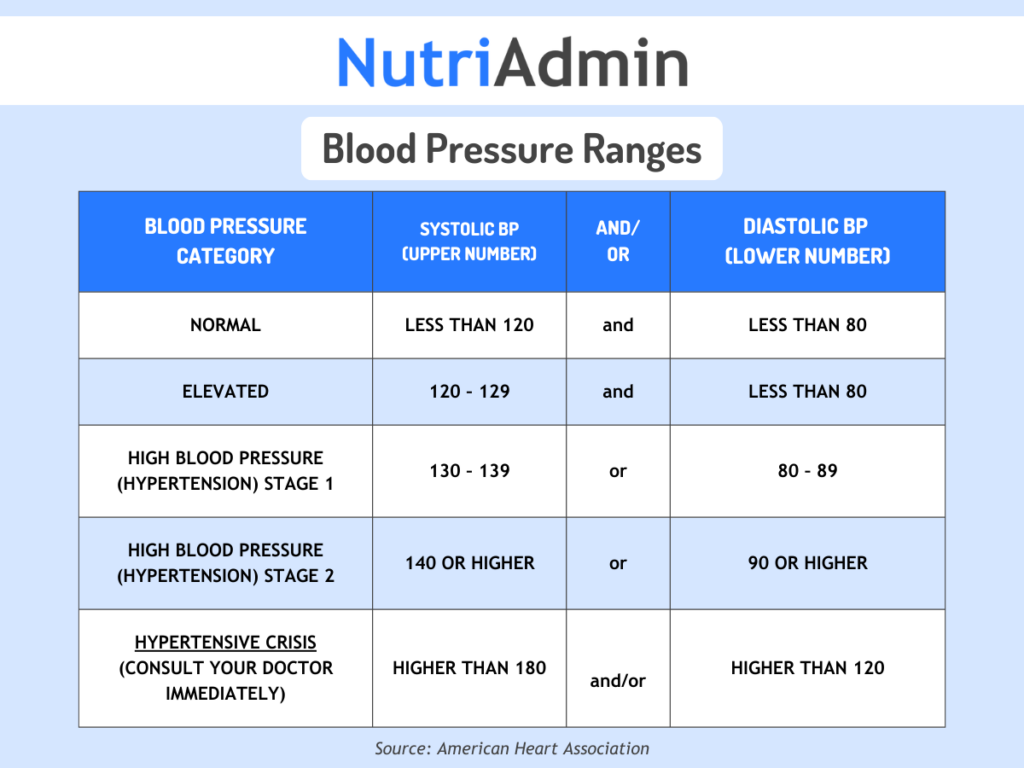
Blood Pressure Table
The American Heart Association categorizes blood pressure as follows:
Blood Pressure Regulation
The blood pressure in humans is well regulated to ensure that organs function well and maintain a balance.
High blood pressure will lead to hypertension with its attendant complications, while low blood pressure will lead to hypotension, which also comes with its complications.
Therefore, regulation of the blood pressure is critical to health. The mechanisms of blood pressure regulation include:
- Nervous system regulation (short-term regulation)
- Renal regulation (Long-term regulation)
Nervous System Regulation of Blood Pressure
When there is a change in blood pressure, the nervous system acts to restore normalcy immediately. It is able to do this by Baroreceptors. Baroreceptors are mechanoreceptors that get activated when the blood vessel is stretched.
Baroreceptors are of two types:
High-pressure baroreceptors are the carotid baroreceptors and the aortic arch baroreceptors. These respond to increased blood pressure and send signals to the nervous system.
Low-pressure baroreceptors are present in the venous system. They sense a decrease in blood volume and pressure and send signals to the nervous system to regulate this pressure.
Renal Regulation of Blood Pressure
Renal Regulation of Blood pressure is achieved by the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS).
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS).
This system is a vital component of blood pressure regulation and is also the target of several medications that are used to treat hypertension.
The RAAS system is slower than the nervous system but achieves more long-term, effective blood pressure regulation.
Renin is a hormone produced in the kidneys in response to low blood pressure. It converts another protein, Angiotensinogen, into Angiotensin I. Angiotensin I is then converted by Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) into Angiotensin II, which then causes the blood vessels to constrict (tighten), leading to higher blood pressure.
Antidiuretic Hormone
ADH is another hormone produced in the hypothalamus (in the brain). It is produced when the body senses a reduction in blood volume and also in response to Angiotensin II. It causes the kidney to absorb more water to increase blood volume and, subsequently, blood pressure.
Aldosterone
Aldosterone is another hormone that is produced in response to low blood pressure and stimulation from Angiotensin. It causes the kidney to absorb more Sodium ions, leading to more absorption of water and a subsequent increase in blood pressure.
From all we have seen, there are so many factors that regulate the blood pressure. All these points are significant in therapy for hypertension. For instance, some antihypertensive medications block the action of aldosterone, so that it cannot cause sodium reabsorption, water absorption, and blood pressure increase.
What Causes Hypertension?
Hypertension is classified into two: Essential and Secondary hypertension.
Essential Hypertension
Essential Hypertension in which there is no obvious cause of elevated blood pressure. Here, hypertension is linked to risk factors like genetic or environmental causes.
Secondary Hypertension
Secondary hypertension: Here, blood pressure rises due to a specific identified cause.
Some of these causes include:
Renal Causes
Diseases that affect the kidneys can lead to hypertension. Renal conditions such as Chronic Kidney disease, Polycystic Kidney disease, Urinary tract obstruction, and Liddle syndrome can all lead to hypertension.
Vascular causes
Blood flows through blood vessels, and when there is a problem with them, it can lead to an increase in blood pressure. Examples of vascular causes include Vasculitis, collagen vascular disease, and coarctation of the aorta.
Endocrine Causes
Endocrine causes may be the most common cause of secondary hypertension. Hormones modulate many of the blood pressure-regulating mechanisms. Hypertension results when there is an excess or deficiency of some of these hormones.
Examples of endocrine causes include Primary hyperaldosteronism, Chromaffin cell tumors, Cushing syndrome, use of oral contraceptives, and exogenous administration of steroids.
Neurogenic Causes
Neurogenic causes of hypertension occur when the nervous system is involved in elevating blood pressure. Some of the common causes are tumors in the brain, autonomic dysfunction, and sleep apnea.
Drugs and Toxins
Some drugs and toxins may directly or directly cause hypertension. Some of these drugs include alcohol, NSAIDs, cocaine, Nicotine, Cyclosporines, and some herbal remedies.
What are the Symptoms of Hypertension?
Hypertension may be present for years in a person without any symptoms. When symptoms do occur, some include:
- Headaches
- Sweating
- Palpitations
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
- Nosebleeds
- Abnormal heart rhythms
What is the Treatment of Hypertension?
The treatment of hypertension involves lifestyle changes and Pharmacology management
Lifestyle changes include:
- Changes in diet
- Weight loss
- Physical activity
- Smoking cessation
Pharmacologic management involves the use of medications to lower blood pressure. The goal of these medications in most people is to have a blood pressure lower than 140/90mmHg.
However, in people with cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, kidney disease, or stroke, the goal is for the blood pressure to be lower than 130/80mmHg.
Some of the standard classes of medications that are used to manage hypertension include:
- ACE Inhibitors
- Angiotensin-2-receptor blockers
- Calcium Channel Blockers
- Diuretics
- Beta Blockers
The first line for treating Hypertension, according to WHO, includes:
- Thiazides
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors or Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
- Calcium channel blockers.
Several times, these drug classes are combined to achieve better blood pressure control. Evidence shows that combination therapy is more effective in lowering systolic blood pressure and has fewer adverse events than monotherapy.
DASH Diet Meal Plan for Hypertension
DASH stands for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension. It is one of the lifestyle changes that physicians may recommend in dealing with hypertension. The focus of this diet is to reduce foods that are high in saturated and trans fat, cholesterol, sweets, processed foods, and sodium while increasing the intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole-grain foods.
How Effective is the DASH Diet Meal Plan for Hypertension?
Scientists have studied the DASH diet over the years, and it has been shown that the DASH diet can reduce systolic blood pressure by as much as 11.5 mmHg in people with hypertension and 7.1 mmHg in individuals without hypertension.
Now, that is a huge win, considering that this works for people of all races and genders.
Furthermore, considering the fact that the maximum systolic blood pressure reduction achieved by antihypertensive medications is 15.5mmHG, the DASH diet makes a strong point for the non-pharmacological management of hypertension.
Moreover, it is very interesting that these changes in blood pressure occurred within 2 weeks of commencing the diet. Studies also show that the DASH diet significantly reduces Uric Acid levels in people with hyperuricemia, improving the symptoms of gout, a painful inflammatory condition.
Again, another study also found that the DASH diet lowers the risk of cardiovascular diseases compared to those who don’t.
Studies also show that the diet may also prevent the development of diabetes and kidney diseases.
Allowed Foods in the DASH Diet Meal Plan
The DASH diet allows the consumption of the following foods:
- Fruits: A variety of fresh or frozen fruits, such as berries, apples, oranges, bananas, and melons.
- Vegetables: A wide array of vegetables, including leafy greens, tomatoes, cucumbers, carrots, and broccoli.
- Whole Grains: Foods like brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat, oats, and whole-grain bread.
- Lean Proteins: Skinless poultry, fish, lean cuts of beef or pork, beans, lentils, and tofu.
- Dairy or Dairy Alternatives: Low-fat or fat-free milk, yogurt, and cheese (or non-dairy alternatives like almond milk).
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and other nuts and seeds in moderation.
- Fats: Healthy fats such as olive oil, avocado, and nut butter should be consumed in moderation.
- Sweets and Added Sugars: Limited intake of sweets and added sugars.
Foods to Avoid in the DASH Diet Meal Plan
Here are some of the foods that the DASH Diet discourages:
- Sodium: Reducing sodium intake is a crucial aspect of the DASH diet. Minimize processed and packaged foods, as well as restaurant meals, often contain high levels of sodium.
- Saturated Fat and Trans Fat: Limit foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as fatty meats, full-fat dairy, and fried items.
- Added Sugars: Foods and beverages with added sugars, like sugary drinks, candies, and desserts in moderation.
- Red Meat: While lean cuts of beef or pork are allowed, excessive consumption of red meat is discouraged due to its potential impact on heart health.

Prevention of Hypertension
Lifestyle changes should not be reserved for the treatment of hypertension. It is possible to prevent hypertension by making lifestyle changes before the blood pressure significantly rises.
Some of the steps to take include:
- Diet: The DASH diet can also prevent hypertension and lower blood pressure. Eat less salty foods and more vegetables.
- Physical activity: WHO recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity weekly.
- Weight loss: Obesity can lead to hypertension.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and can lead to hypertension
- Alcohol: Excess alcohol can elevate the blood pressure
- Avoid missing medications for those already taking them.
DASH Diet Meal Plan
Clients may request their nutritionists, dieticians, or coaches to create a meal plan for the DASH diet. The process of making a meal plan is straightforward for professionals but can be time-consuming when they need to create several meal plans.
Several meal apps have made this process seamless and less cumbersome. NutriAdmin is a meal plan generator that creates custom DASH diet meal plans. It is software for nutritionists, dietitians, and coaches who want to create meal plans for their clients as soon as possible.
Here is a sample DASH Diet Meal Plan generated with NutriAdmin:
Mediterranean and DASH Diets
The Mediterranean diet is a healthy eating plan based on the traditional diets of countries around the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Spain, and Italy. It focuses on consuming vegetables, beans, nuts, olive oil, seafood, fruits, and legumes while minimizing the consumption of added sugars, red meat, and processed foods.
Both the Mediterranean diet and the DASH diet emphasize that individuals should consume whole grains, vegetables, and fruits. However, the Mediterranean diet allows dairy consumption, red meat, sweets, and alcohol in moderation, while the DASH diet outright disallows them.
The Mediterranean diet is also based on staple foods of countries in the Mediterranean area, while the DASH diet has a broader scope of foods.
Despite their differences, both diets have several benefits, including reducing blood pressure, anti-inflammatory effects, cardiovascular disease risk reduction, and weight loss.
Hence, they both have very good eating patterns when it comes to living healthy and, more specifically, lowering blood pressure.
DASH Diet Recipes
NutriAdmin is also an effective recipe software that can help you generate healthy recipes for high blood pressure. It has an extensive recipe database that provides a wide variety of food combinations, including their ingredients, instructions, and nutrient analysis.
Here are some recipes in the DASH diet that are great for hypertension generated by NutriAdmin.
Conclusion
Hypertension is a pervasive and serious health issue, affecting over a billion people worldwide. Often undiagnosed due to its asymptomatic nature, it poses significant risks for cardiovascular diseases, stroke, and kidney disorders. Understanding hypertension, its causes, and its symptoms is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Addressing hypertension requires a multifaceted approach, combining lifestyle changes and pharmacological treatments. The DASH diet stands out as a highly effective non-pharmacological strategy, demonstrating significant reductions in blood pressure and offering additional health benefits, such as lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases and improving symptoms of conditions like gout.
Moreover, integrating healthy eating patterns, regular physical activity, and smoking cessation into daily routines can greatly enhance the control of blood pressure. While medications remain essential for many, lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in achieving optimal blood pressure levels and reducing the dependency on pharmacological interventions.
By raising awareness and encouraging proactive measures, we can combat the silent menace of hypertension, improving health outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for millions of people globally. Through education, early detection, and comprehensive management strategies, the burden of hypertension can be significantly alleviated, paving the way for a healthier future.