As nutrition and fitness professionals, helping clients manage hunger effectively is one of the biggest challenges in supporting lasting behavior change. Satiety, or the feeling of fullness after eating, is a critical factor that influences how much people eat and how satisfied they feel between meals. One of the most effective strategies to support appetite control and sustainable nutrition is incorporating high volume low calorie foods into meals.
These foods allow clients to enjoy satisfying portions that promote fullness without excess calorie intake. When combined with a focus on nutrient dense foods, this approach not only curbs hunger but also ensures clients receive essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
In this article, we’ll explore what high volume low calorie foods are, why they matter, and how to use them in practice. We’ll also provide plenty of practical examples of low calorie nutrient dense foods to help you guide your clients toward better satiety and sustainable eating habits.
What Are High Volume Low Calorie Foods?
At its core, the concept of high volume low calorie foods revolves around energy density—the number of calories per gram or serving of food.
Foods that are low in calories but high in volume typically contain a lot of water, fiber, or air. This means clients can eat larger portions that physically fill the stomach, triggering feelings of fullness and satisfaction without consuming too many calories.
For instance, a generous chicken and mixed vegetable salad dressed with a light vinaigrette will satisfy hunger more effectively than a small portion of creamy pasta salad or a handful of potato chips with the same calorie content.
Importantly, volume eating isn’t just about eating “empty” bulk. The best high volume foods are also low calorie nutrient dense foods—meaning they pack a powerful punch of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, supporting overall health and performance.
Pros and Cons of High Volume Low Calorie Foods
Pros
- Enhanced Satiety and Appetite Control: High volume low calorie foods contain plenty of water and fiber. These components fill the stomach and activate fullness signals. This helps clients eat less without feeling hungry.
- Weight Management Support: Research shows that diets emphasizing low energy density foods can help reduce calorie intake naturally. This makes fat loss easier and more sustainable
- Rich in Nutrients: These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They support immune health and reduce inflammation. Nutrient density helps prevent deficiencies during calorie restriction.
- Improved Digestive Health: High fiber content promotes regular bowel movements. Fiber also supports a healthy gut microbiome. It slows digestion, stabilizing blood sugar and extending fullness.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Fiber and water slow glucose absorption. This prevents blood sugar spikes and crashes. Stable blood sugar helps control hunger and cravings.
- Psychological Satisfaction: Large portions of colorful fruits and vegetables can make meals more enjoyable. This reduces feelings of restriction. Enjoyable meals improve long-term adherence.
Cons
- Risk of Inadequate Calorie Intake for Some Clients: Highly active clients or athletes may struggle to meet energy needs. Relying too much on low calorie foods can cause insufficient calorie intake.
- Protein Intake Considerations: While many high volume foods are nutrient dense, they tend to be low in protein. Without careful planning, clients might not consume enough protein to support muscle maintenance, satiety, and recovery.
- Potential for Monotony or Palatability Issues: Some clients might find large portions of vegetables or broth-based foods bland. This can reduce motivation to stick with the diet. Using herbs, spices, and varied cooking methods helps.
- Nutrient Imbalances if Not Well-Rounded: Overemphasizing low calorie foods without balancing fats and protein can cause nutrient deficiencies. Essential fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins may be lacking.
- Gastrointestinal Sensitivity: Many high volume low calorie foods are usually high in fiber. This may cause bloating, gas, or discomfort for individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or other digestive sensitivities. Gradual fiber increase and avoiding triggers is recommended.
Examples of Nutrient Dense Low Calorie Foods
Here are some practical examples of nutrient-dense, low-calorie foods to include in your clients’ meals. Including these in your clients’ diets can help increase satiety and improve overall nutrient intake. They’re versatile and easy to incorporate at any meal.
Vegetables
Vegetables are the cornerstone of high volume low calorie eating. Most non-starchy vegetables contain fewer than 50 calories per serving but are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Leafy Greens: spinach, kale, arugula, Swiss chard, collard greens, lettuce, celery.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: radish, turnip, cauliflower, Brussel sprouts, cabbage, broccoli.
- Other: zucchini, cucumber, bell pepper, asparagus, mushrooms, tomato, eggplant, green beans, alfalfa sprouts.
Fruits
Fruits provide natural sweetness and fiber with relatively low calories, especially berries and melons.
- Berries: strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, blackberries.
- Melons: watermelon, cantaloupe, honeydew.
- Citrus: oranges, grapefruit, lemons, limes.
- Other: Apples, pears, peaches.
Legumes and Pulses
While legumes have more calories than vegetables, they are still considered foods high in nutrients low in calories relative to their satiety and nutrient profile. The following are calories per 100 grams:
- Lentils: 116 kcal
- Chickpeas: 164 kcal
- White Beans: 139 kcal
- Black Beans: 132 kcal
- Navy Beans: 140 kcal
- Pinto Beans: 143 kcal

Broth-Based Soups
Soups made with vegetable or bone broth are excellent for increasing meal volume without adding many calories.
- Vegetable broth with mixed veggies: Typically under 50 calories per cup but very filling if you add protein sources.
- Miso soup: Usually under 100 calories per cup, contains probiotics for gut health.
- Chicken or bone broth: Around 50 calories per cup, rich in collagen and minerals.

Lean Proteins (Moderate Volume, Low Calorie)
While these are not high volume in the same way vegetables are, combining lean proteins with high volume low calorie foods creates balanced meals that promote satiety and muscle preservation.
- Skinless chicken breast (grilled): 148 kcal per 100g
- White fish (cod, haddock): 70-90 kcal per 100g
- Egg whites: 52 kcal per 100g
- Low-fat Greek yogurt: 67 kcal per 100g, adds creaminess and probiotics.

Other High Volume Foods
- Popcorn (air-popped): About 31 calories per cup, high fiber and volume.
- Unsweetened gelatin
Why Nutrient Density Matters
Focusing on low calorie nutrient dense foods is not just about reducing calories. It is also about maximizing the quality of those calories. Nutrient density ensures clients get the vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber needed to support:
- Weight Management: Adequate vitamins and minerals help maintain metabolic functions, hormone balance, and lean body mass during calorie restriction.
- Chronic Disease Prevention: Diets high in fruits, vegetables, and legumes reduce risks for cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Performance and Recovery: Micronutrients like iron, magnesium, and B vitamins are essential for energy metabolism and muscle function.
- Gut Health: Fiber-rich foods feed beneficial gut bacteria, which influence inflammation, immunity, and even mood.
- Long-Term Adherence: Nutrient-dense foods reduce cravings and improve satisfaction, making healthy eating sustainable.
How to Use These Foods in Practice
Here are actionable tips for nutrition and fitness professionals to incorporate high volume low calorie foods into client programs.
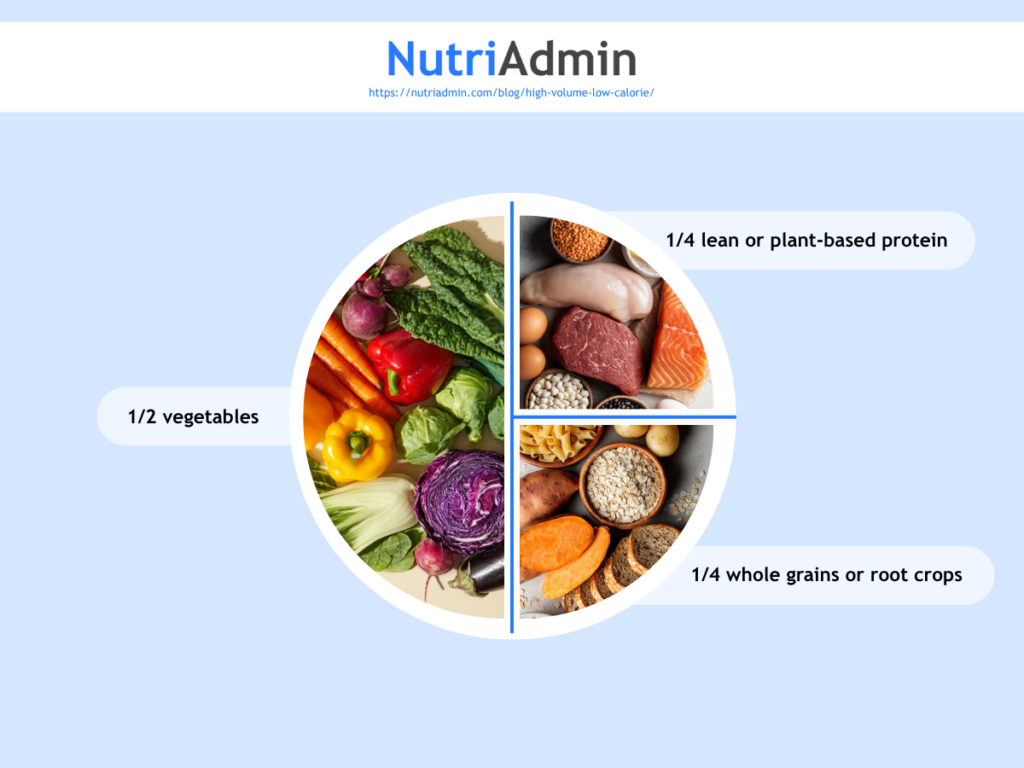
Plate Method
Encourage clients to fill half their plate with non-starchy vegetables, one-quarter with lean protein, and one-quarter with whole grains or starchy vegetables.
This balanced approach increases fiber and nutrient intake, which supports digestion and helps control blood sugar levels. Lean protein promotes muscle maintenance and satiety, reducing overeating. Whole grains and starchy vegetables provide sustained energy and essential nutrients.
Start Meals with Soup or Salad
Eating a broth-based vegetable soup or salad before the main course can reduce total calorie intake by promoting early satiety.
Combine Fiber and Protein
Pairing legumes or lean proteins with high volume vegetables maximizes satiety and supports muscle maintenance.
Snack Smart
For satisfying snacks that add volume without too many calories, try pairing raw vegetables with hummus or fresh berries with low-fat yogurt. These combinations provide a good balance of protein and fiber, helping to keep hunger at bay while supporting fullness and nutrition.
Mindful Eating
Teach clients to eat slowly and pay attention to fullness signals, which are enhanced when consuming high volume foods.
Hydrate with Low-Calorie Beverages
Water, herbal teas, and infused water add volume and support hydration without excess calories.
High Volume Low Calorie Foods in NutriAdmin
NutriAdmin is a powerful tool for nutritionists, dietitians, coaches, and personal trainers to create personalized, nutrient-dense meal plans that emphasize high volume low calorie foods. Here’s how it can support your practice:
Create Personalized Meal Plans
Create personalized meal plans that emphasize high-volume, low-calorie foods while accurately tracking calories, macronutrients, and micronutrients. NutriAdmin’s meal plan generator makes it easy to set calorie goals and macronutrient targets. You can also exclude ingredients your clients need to avoid or dislike, and further customize plans by selecting cooking equipment, preparation and cooking times, and preferred cuisines.
This streamlined process lets you deliver tailored, nutritious meal plans your clients will appreciate—all in just 60 seconds, saving you valuable time without compromising quality.
If you prefer to use your own recipes, NutriAdmin’s meal plan and recipe management features give you full control to customize every plan. You can build meal plans from scratch with your personal recipes, use the meal plan generator, or combine both your recipes and NutriAdmin’s nutritionist-vetted recipe database. This flexibility ensures you create truly personalized meal plans tailored to your clients’ unique needs.
Summary
High volume low calorie foods offer a simple yet effective way to help clients manage hunger and improve nutrient intake. When clients learn to fill their plates with these satisfying, nutrient-dense options, they’re more likely to stick with their nutrition plans and feel energized throughout the day.
By combining this approach with personalized coaching and meal planning, you create a roadmap for clients to build lasting, healthy habits. Using platforms like NutriAdmin streamlines this process, giving you the flexibility to tailor plans that fit individual preferences and lifestyles. Adopting this strategy can lead to lasting improvements in both client satisfaction and health outcomes.