As the health and wellness industry continues to evolve, one topic frequently discussed is superfoods. But what exactly are superfoods, and how do they contribute to overall health? In this blog post, we will explore the concept of superfoods and define their key characteristics. We will also highlight the top 10 foods commonly labeled as superfoods, along with their health and nutritional benefits.
What Are Superfoods?
While there’s no official scientific classification for superfoods, the common traits include high nutrient density and potential health benefits. Foods like blueberries, kale, quinoa, and chia seeds frequently find their way onto superfood lists due to their impressive nutrient content. These foods often contain antioxidants, essential fatty acids, and phytochemicals with anti-inflammatory properties.
For nutrition and fitness professionals, a deep understanding of superfoods is crucial. It enables them to guide clients effectively, helping them to establish realistic expectations on the health benefits that these foods can offer.
Common Characteristics
- Nutrient Density: Superfoods deliver an abundance of vitamins and minerals compared to their calorie count.
- Antioxidants: Packed with antioxidants that help neutralize free radicals, potentially lowering the risk of chronic conditions like heart disease and cancer.
- Anti-Inflammatory Benefits:
- Fiber-Rich: They often contain substantial amounts of dietary fiber that aids digestion, helps regulate blood sugar levels, and contributes to satiety.
- Healthy Fats: Many provide sources of healthy fats, such as omega-3 which are essential for brain and cardiovascular health.
How Marketing Influences Our Perception of Superfoods
Marketing plays a crucial role in shaping our views on superfoods. Advertisements often emphasize their exceptional health benefits, suggesting that these foods can cure diseases or provide miraculous boosts to our well-being, which may lead to unrealistic expectations.
The rise of social media and health trends has further amplified this effect, as influencers showcase superfoods with appealing visuals, creating a perception that they are essential for a healthy lifestyle. Additionally, celebrity endorsements can significantly boost the popularity of these foods, often without sufficient scientific backing to support their claims.

The term “superfood” itself can be misleading, implying that a single food can dramatically enhance health and overshadowing the importance of a balanced diet. While many superfoods are nutritious and offer various health benefits, the marketing surrounding them can create misconceptions.
For nutrition professionals, it’s vital to discern the difference between genuine health benefits and marketing hype. Educating clients about the importance of a balanced diet and the role of a variety of foods is essential to combat misunderstandings related to the superfood phenomenon. Instead of relying solely on trendy superfoods, consumers should focus on informed choices that promote overall health.
Top 10 Superfoods: Facts vs. Hype
When it comes to the most popular superfoods, like kale, salmon, blueberries, and quinoa, there is often a mix of fact and hype. While many of these foods have proven health benefits supported by scientific evidence, it’s essential to approach them with realistic expectations.
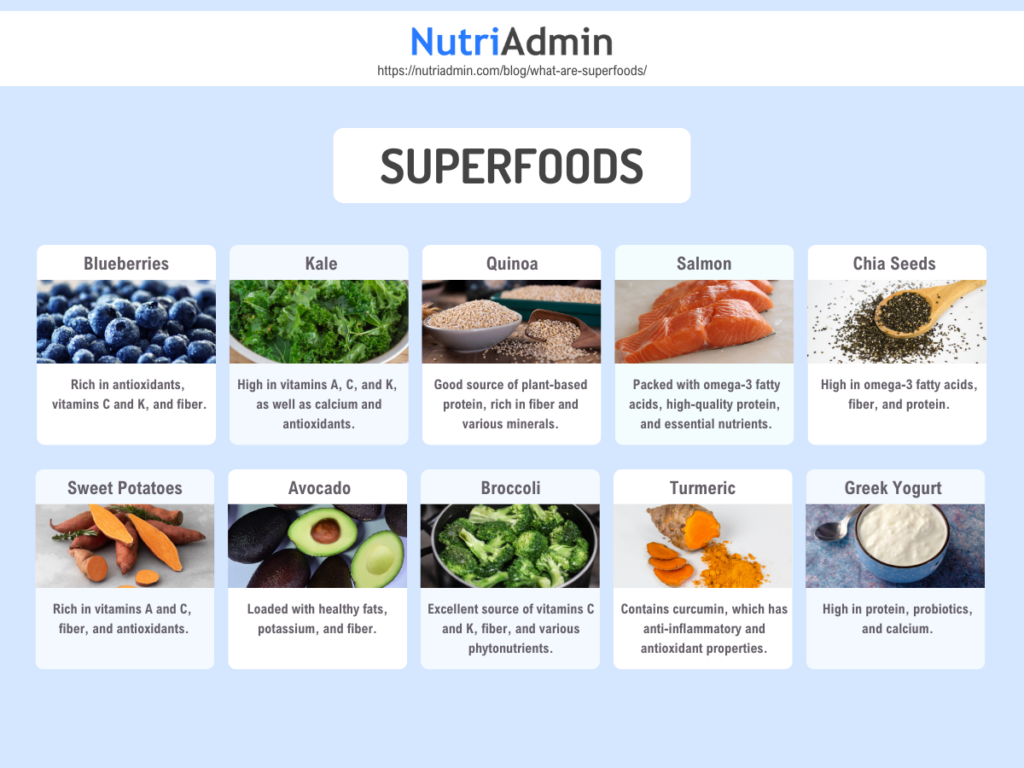
Blueberries
Rich in phytochemicals, particularly anthocyanins, which provide their distinctive color. Also abundant in vitamins C and K, as well as dietary fiber.
Studies suggest that regularly eating blueberries or anthocyanins may lower the risk of heart disease, death, and type 2 diabetes, and can also help with weight management and brain health.
Kale
A powerhouse of nutrients, including fiber, vitamins A, C, K, B6, folate, and manganese. It also contains numerous phytochemicals such as phenolics, glucosinolates, and carotenoids.
Quinoa
Quinoa is a gluten-free grain that serves as an excellent source of protein, containing all nine essential amino acids. It is rich in fiber, magnesium, vitamin B1, along with various minerals.
Additionally, quinoa contains a variety of phytochemicals, including saponins, phenolic compounds, phytoecdysteroids, betalains, and phytosterols. These phytochemicals offer several benefits, such as antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory properties, cholesterol reduction, and antidiabetic effects.
Salmon
An excellent source of high-quality protein, omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA), vitamin D, and selenium.
Omega-3 fatty acids are vital for maintaining heart health by lowering triglycerides, reducing blood pressure, and preventing plaque formation in arteries.
Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, protein, and essential nutrients like calcium and zinc. Omega-3 fatty acids support heart health by lowering cholesterol, regulating blood pressure, preventing clots, and reducing inflammation.
The insoluble fiber and mucilage in chia seeds help lower LDL cholesterol and regulate digestion, which can stabilize blood sugar levels and enhance satiety.
Sweet Potatoes
Rich in vitamins A (from beta-carotene), C, potassium, and dietary fiber, along with a variety of antioxidants. They promote digestive health due to their high fiber content.
Avocado
Loaded with heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, potassium, vitamin E, and fiber. Avocados are known to help lower bad cholesterol levels (LDL) while raising good cholesterol (HDL). They also provide essential nutrients which support heart health and contribute to healthy skin.
Broccoli
Broccoli is rich in vitamin C, which enhances immune function, supports collagen production, aids in wound healing, and improves iron absorption. It serves as a good source of calcium, crucial for strong bones and osteoporosis prevention, and is also high in vitamin K for bone health.
Low in calories yet high in fiber, broccoli promotes fullness, helps with weight management, and supports a healthy metabolism. Its fiber content also aids digestion, regulates bowel movements, and fosters a healthy gut microbiome.
Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin which is known for its potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
However, studying its effects is challenging due to its instability and low bioavailability when consumed. Additionally, variations in curcumin products can complicate studies, resulting in unclear conclusions about their health benefits.
Greek Yogurt
Greek yogurt is a nutrient-dense food that is high in protein, making it great for muscle support and satiety. It contains probiotics, which promote gut health, along with calcium for strong bones and potassium for heart health. Additionally, Greek yogurt typically has lower sugar content and higher protein content compared to regular yogurt.
Are superfoods really “super”?
These superfoods are undoubtedly nutritious and can be great additions to a person’s diet. However, it is always important to keep in mind that no single food can provide all the essential nutrients needed by our body and can guarantee optimal health.
Incorporating superfoods into client meal plans can provide substantial health benefits. As nutrition and fitness professionals, it’s essential to emphasize the importance of a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods, rather than focusing solely on isolated “super” items.
By understanding what superfoods are and how they contribute to superfood health, you can better guide your clients towards making informed dietary choices that support their health and fitness goals.
Recipes with Superfoods
NutriAdmin has a database of nutritious recipes, including those that incorporate various superfoods. You can download free recipes from the NutriAdmin database below.